
|
|
PDF MC34115 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | MC34115 | |
| Descripción | CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE SLOPE DELTA MODULATOR/DEMODULATOR | |
| Fabricantes | Motorola Semiconductors | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de MC34115 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 16 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
www.DataSheet4U.com
Order this document by MC34115/D
MC34115
Continuously Variable Slope
Delta Modulator/Demodulator
Providing a simplified approach to digital speech encoding/decoding, the
MC34115 CVSD is designed for speech synthesis and commercial telephone
applications. A single IC provides both encoding and decoding functions.
• Encode and Decode Functions Selectable with a Digital Input
• Utilization of Compatible I2L – Linear Bipolar Technology
• CMOS Compatible Digital Output
• Digital Input Threshold Selectable (VCC/2 Reference Provided On–Chip)
• 3–Bit Algorithm
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE
SLOPE DELTA
MODULATOR/DEMODULATOR
SEMICONDUCTOR
TECHNICAL DATA
16
1
P SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 648
CVSD Block Diagram
Encode/Decode
Clock
15 14
Analog Input
Analog
Feedback
1
2
–
+
Digital 13
Data Input
–
+
Digital 12
Threshold
Vth
3–Bit
Shift Register
QQQQQQ
VCC
16
9
Digital Output
10
VCC/2 Output
VCC/2
Ref
IRef
IO
Integrator
Amplifier
–
+
Logic
Slope
Polarity
Switch
IInt
11 Coincidence
Output
V/I
Converter
3 Syllabic Filter
4 Gain Control
IGC
7 56
Analog Ref Filter
Output Input Input
(+) (–)
8
VEE
This device contains 144 active transistors.
16
1
DW SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 751G
(SO–16L)
PIN CONNECTIONS
Analog Input (–) 1
Analog Feedback (+) 2
Syllabic Filter 3
Gain Control 4
Ref Input (+) 5
Filter Input (–) 6
Analog Output 7
VEE 8
16 VCC
15 Encode/Decode
14 Clock
13 Digital Data Input (–)
12 Digital Threshold
11 Coincidence Output
10 VCC/2 Output
9 Digital Output
(Top View)
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device
Operating
Temperature Range
Package
MC34115P
TA = 0° to +70°C
MC34115DW
Plastic DIP
SO–16L
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
© Motorola, Inc. 1996
Rev 1
1
1 page 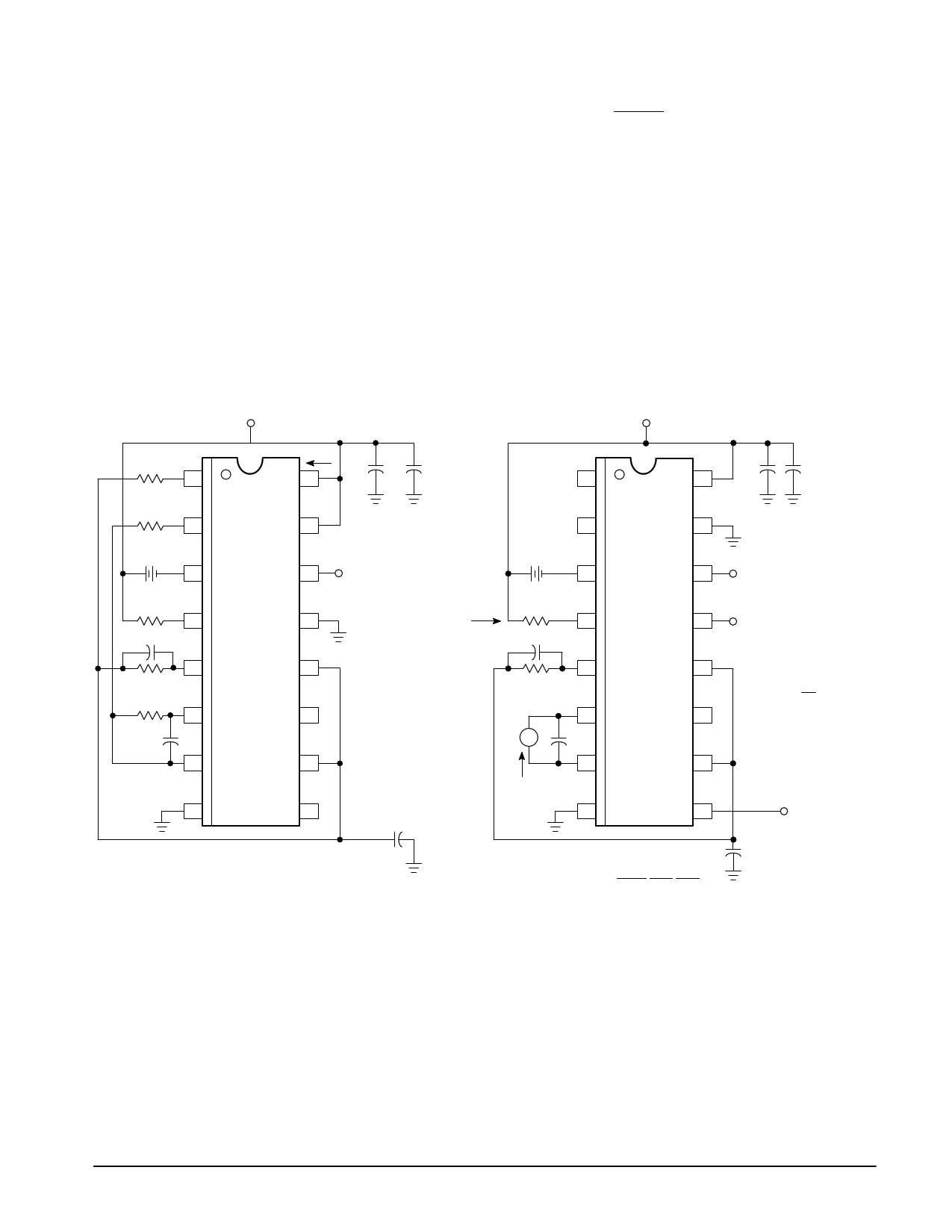
MC34115
Pin 13 – Digital Data Input
In a decode application, the digital data stream is applied
to Pin 13. In an encoder it may be unused or may be used to
transmit a signaling message under the control of Pin 15. It is
an inverting input with respect to Pin 9. When Pins 9 and 13
are connected, a toggle flip–flop is formed and a forced idle
channel pattern can be transmitted. The digital data input
level should be maintained for 0.5 µs before and after the
clock trigger for proper clocking.
Pin 14 – Clock Input
The clock input determines the data rate of the codec
circuit. A 16 k bit rate requires a 16 kHz clock. The switching
threshold of the clock input is set by Pin 12. The shift register
circuit toggles on the falling edge of the clock input. The
minimum high time for the clock input is 300 ns and minimum
low time is 900 ns.
Pin 15 – Encode/Decode
This pin controls the connection of the analog input
comparator and the digital input comparator to the internal
shift register. If high, the result of the analog comparison will
be clocked into the register on the falling edge at Pin 14. If low,
the digital input state will be entered. This allows use of the IC
as an encoder/decoder or simplex codec without external
parts. Furthermore, it allows non–voice patterns to be forced
onto the transmission line through Pin 13 in an encoder.
Pin 16 – VCC
The power supply range is from 4.75 to 16.5 V between
Pin VCC and VEE.
Figure 1. Power Supply Current
VCC
1.0 k
1
1.0 k
60 mV
+–
2
3
5.0 k
4
0.1
5
10 k
10 k
6
0.05
7
ICC 10 µF
16
15
14 Clock
CVSD
MC34115
13
12
11
10
0.1
89
0.1
Figure 2. IGCR – Gain Control Range and IInt –
Integrating Current
VCC
10 µF
0.1
1 16
VB
+–
2
3
IGC Rx
4
0.1
5
10 k
A
IInt
6
0.05
7
8
15
14
CVSD
MC34115
13
12
11
10
9
Clock
(Note 2)
Digital Data
Input
IGC +
VB
Rx
Rx v 5.0 k
Digital
Output
(Note 1)
0.1
NOTES: 1. Digital Output = Digital Data Input
2. For static testing, the clock is only necessary for
preconditioning to obtain proper state for a given input.
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
5
5 Page 
MC34115
Figure 15. 16 kHz Simplex Voice Codec
(Using MC34115, Single–Pole Companding and Single Integration)
Push
To Talk
Key
5.0
(Norm
Open)
10 k
Analog
Input
+
4.0 µF
Encode/Decode 15
1 Comp
–
2
+
Digital Input
Digital Output
Clock 16 kHz
5.0
Digital
Out 9 Clock 14 VCC 16
13
–
600 600 12
+
Vth
Shift
Register
0.1 1.0 k 10 k
Analog
Output
10
5
Ref
Input
7
Analog
Out
VCC/2
Ref
+
–
Logic
Slope Polarity
Switch
Coin
Out
11
Syl RS
In
3
GC
4
3.3 k RP
18 k CS
0.33
2.4 M Rmin
1.3 k Rx
C1 0.1
R1 10 k
Filter 6
Ref
VEE 8
VS
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
CVSD DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
A simple CVSD encoder using the MC34115 is shown in
Figure 15. This IC is a general purpose CVSD building block
which allows the system designer to tailor the encoder’s
transmission characteristics to the application. Thus, the
achievable transmission capabilities are constrained by the
fundamental limitations of delta modulation and the design of
encoder parameters. The performance is not dictated by the
internal configuration of the MC34115. There are six design
considerations involved in designing these basic CVSD
building blocks into a specific codec application.
These are listed below:
1. Selection of clock rate
2. Selection of loop gain
3. Selection of minimum step size
4. Design of integration filter transfer function
5. Design of syllabic filter transfer function
6. Design of low pass filter at the receiver
The circuit in Figure 15 is the most basic CVSD circuit
possible. For many applications in secure radio or other
intelligible voice channel requirements, it is entirely sufficient.
In this circuit, items 4 and 5 are reduced to their simplest
form. The syllabic and integration filters are both single–pole
networks. The selection of items 1 through 3 govern the
codec performance.
Layout Considerations
Care should be exercised to isolate all digital signal paths
(Pins 9, 11, 13 and 14) from analog signal paths (Pins 1 to 7
and 10) in order to achieve proper idle channel performance.
Clock Rate
With minor modifications, the circuit in Figure 15 may be
operated anywhere from 9.6 to 64 kHz clock rates. Obviously
the higher the clock rate the higher the S/N performance. The
circuit in Figure 15 typically produces the S/N performance
shown in Figure 16. The selection of clock rate is usually
dictated by the bandwidth of the transmission medium. Voice
bandwidth systems will require no higher than 9600 Hz.
Some radio systems will allow 12 kHz. Private 4–wire
telephone systems are often operated at 16 kHz and
commercial telephone performance can be achieved at
32 k bits and above.
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 16 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet MC34115.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| MC3411 | P-Channel 20-V (D-S) MOSFET | Freescale |
| MC34114 | TELEPHONE SPEECH NETWORK WITH DIALER INTERFACE | Motorola Semiconductors |
| MC34115 | CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE SLOPE DELTA MODULATOR/DEMODULATOR | Motorola Semiconductors |
| MC34117 | Telephone Tone Riger | Motorola Semiconductors |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
