
|
|
PDF M25P10-A Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | M25P10-A | |
| Descripción | 1 Mbit/ Low Voltage/ Serial Flash Memory With 25 MHz SPI Bus Interface | |
| Fabricantes | STMicroelectronics | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de M25P10-A (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
M25P10-A
1 Mbit, Low Voltage, Serial Flash Memory
With 25 MHz SPI Bus Interface
FEATURES SUMMARY
s 1 Mbit of Flash Memory
s Page Program (up to 256 Bytes) in 1.5ms
(typical)
s Sector Erase (256 Kbit) in 2 s (typical)
s Bulk Erase (1 Mbit) in 3 s (typical)
s 2.7 V to 3.6 V Single Supply Voltage
s SPI Bus Compatible Serial Interface
s 25 MHz Clock Rate (maximum)
s Deep Power-down Mode 1 µA (typical)
s Electronic Signature (10h)
s More than 100,000 Erase/Program Cycles per
Sector
s More than 20 Year Data Retention
Figure 1. Packages
8
1
SO8 (MN)
150 mil width
VFQFPN8 (MP)
(MLP8)
ENHANCED VERSION OF THE M25P10
This device is an enhanced version of the
M25P10. The enhanced features include: larger
page size, shorter programming time, higher clock
frequency.
February 2003
1/34
1 page 
M25P10-A
OPERATING FEATURES
Page Programming
To program one data byte, two instructions are re-
quired: Write Enable (WREN), which is one byte,
and a Page Program (PP) sequence, which con-
sists of four bytes plus data. This is followed by the
internal Program cycle (of duration tPP).
To spread this overhead, the Page Program (PP)
instruction allows up to 256 bytes to be pro-
grammed at a time (changing bits from 1 to 0), pro-
vided that they lie in consecutive addresses on the
same page of memory.
Sector Erase and Bulk Erase
The Page Program (PP) instruction allows bits to
be reset from 1 to 0. Before this can be applied, the
bytes of memory need to have been erased to all
1s (FFh). This can be achieved either a sector at a
time, using the Sector Erase (SE) instruction, or
throughout the entire memory, using the Bulk
Erase (BE) instruction. This starts an internal
Erase cycle (of duration tSE or tBE).
The Erase instruction must be preceeded by a
Write Enable (WREN) instruction.
Polling During a Write, Program or Erase Cycle
A further improvement in the time to Write Status
Register (WRSR), Program (PP) or Erase (SE or
BE) can be achieved by not waiting for the worst
case delay (tW, tPP, tSE, or tBE). The Write In
Progress (WIP) bit is provided in the Status Regis-
ter so that the application program can monitor its
value, polling it to establish when the previous
Write cycle, Program cycle or Erase cycle is com-
plete.
Active Power, Stand-by Power and Deep
Power-Down Modes
When Chip Select (S) is Low, the device is en-
abled, and in the Active Power mode.
When Chip Select (S) is High, the device is dis-
abled, but could remain in the Active Power mode
until all internal cycles have completed (Program,
Erase, Write Status Register). The device then
goes in to the Stand-by Power mode. The device
consumption drops to ICC1.
The Deep Power-down mode is entered when the
specific instruction (the Enter Deep Power-down
Mode (DP) instruction) is executed. The device
consumption drops further to ICC2. The device re-
mains in this mode until another specific instruc-
tion (the Release from Deep Power-down Mode
and Read Electronic Signature (RES) instruction)
is executed.
All other instructions are ignored while the device
is in the Deep Power-down mode. This can be
used as an extra software protection mechanism,
when the device is not in active use, to protect the
device from inadvertant Write, Program or Erase
instructions.
Status Register
The Status Register contains a number of status
and control bits, as shown in Table 5, that can be
read or set (as appropriate) by specific instruc-
tions.
WIP bit. The Write In Progress (WIP) bit indicates
whether the memory is busy with a Write Status
Register, Program or Erase cycle.
WEL bit. The Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit indi-
cates the status of the internal Write Enable Latch.
BP1, BP0 bits. The Block Protect (BP1, BP0) bits
are non-volatile. They define the size of the area to
be software protected against Program and Erase
instructions.
SRWD bit. The Status Register Write Disable
(SRWD) bit is operated in conjunction with the
Write Protect (W) signal. The Status Register
Write Disable (SRWD) bit and Write Protect (W)
signal allow the device to be put in the Hardware
Protected mode. In this mode, the non-volatile bits
of the Status Register (SRWD, BP1, BP0) become
read-only bits.
5/34
5 Page 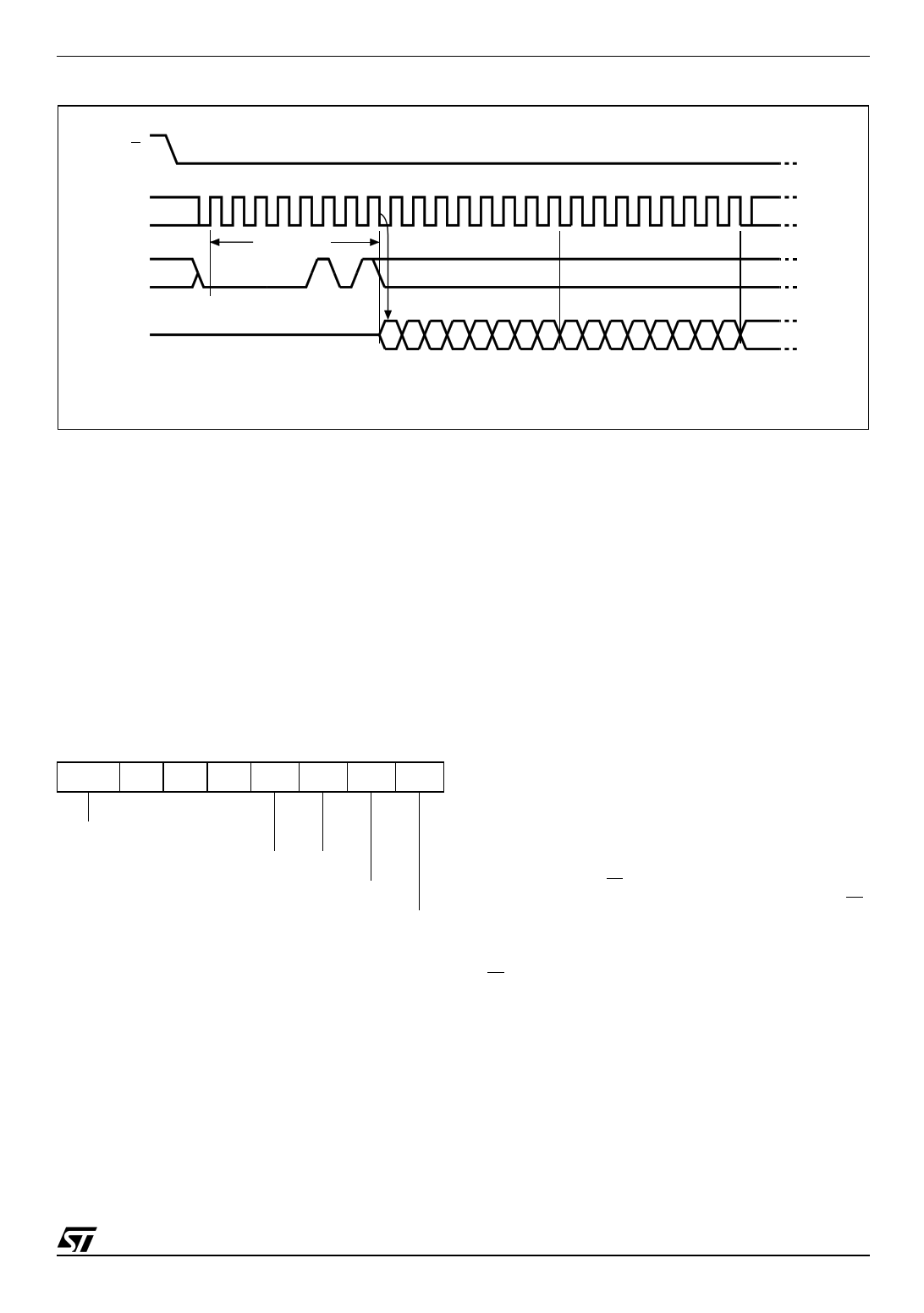
M25P10-A
Figure 10. Read Status Register (RDSR) Instruction Sequence and Data-Out Sequence
S
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
C
Instruction
D
Status Register Out
Status Register Out
High Impedance
Q 76543210765432107
MSB
MSB
AI02031E
Read Status Register (RDSR)
The Read Status Register (RDSR) instruction al-
lows the Status Register to be read. The Status
Register may be read at any time, even while a
Program, Erase or Write Status Register cycle is in
progress. When one of these cycles is in progress,
it is recommended to check the Write In Progress
(WIP) bit before sending a new instruction to the
device. It is also possible to read the Status Reg-
ister continuously, as shown in Figure 10.
Table 5. Status Register Format
b7 b0
SRWD 0 0 0 BP1 BP0 WEL WIP
Status Register Write Protect
Block Protect Bits
Write Enable Latch Bit
Write In Progress Bit
The status and control bits of the Status Register
are as follows:
WIP bit. The Write In Progress (WIP) bit indicates
whether the memory is busy with a Write Status
Register, Program or Erase cycle. When set to 1,
such a cycle is in progress, when reset to 0 no
such cycle is in progress.
WEL bit. The Write Enable Latch (WEL) bit indi-
cates the status of the internal Write Enable Latch.
When set to 1 the internal Write Enable Latch is
set, when set to 0 the internal Write Enable Latch
is reset and no Write Status Register, Program or
Erase instruction is accepted.
BP1, BP0 bits. The Block Protect (BP1, BP0) bits
are non-volatile. They define the size of the area to
be software protected against Program and Erase
instructions. These bits are written with the Write
Status Register (WRSR) instruction. When one or
both of the Block Protect (BP1, BP0) bits is set to
1, the relevant memory area (as defined in Table
2) becomes protected against Page Program (PP)
and Sector Erase (SE) instructions. The Block
Protect (BP1, BP0) bits can be written provided
that the Hardware Protected mode has not been
set. The Bulk Erase (BE) instruction is executed if,
and only if, both Block Protect (BP1, BP0) bits are
0.
SRWD bit. The Status Register Write Disable
(SRWD) bit is operated in conjunction with the
Write Protect (W) signal. The Status Register
Write Disable (SRWD) bit and Write Protect (W)
signal allow the device to be put in the Hardware
Protected mode (when the Status Register Write
Disable (SRWD) bit is set to 1, and Write Protect
(W) is driven Low). In this mode, the non-volatile
bits of the Status Register (SRWD, BP1, BP0) be-
come read-only bits and the Write Status Register
(WRSR) instruction is no longer accepted for exe-
cution.
11/34
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet M25P10-A.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| M25P10-A | 1 Mbit/ Low Voltage/ Serial Flash Memory With 25 MHz SPI Bus Interface | STMicroelectronics |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
